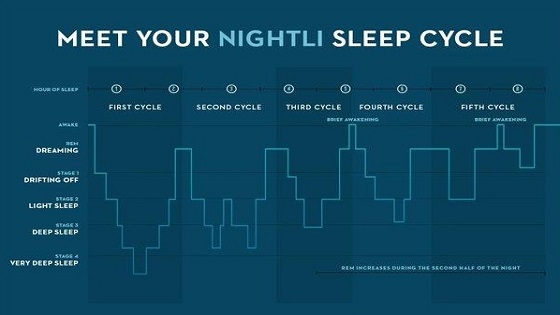
The sleep cycle is the process in which a person goes from light to deep sleep and is also called the sleep-dream cycle. It takes about 70 to 110 minutes for an adult to go through the sleep cycle and it is divided into two stages, REM (rapid eye movement) and slow wave sleep.
REM sleep
REM sleep is a stage of the sleep cycle when the body is in deep sleep. It is marked by a marked decrease in muscle tone, a slowing of breathing, and a slowed heart rate.
REM sleep is a special type of sleep that is associated with dreaming. People who do not get enough REM sleep often have difficulty recalling skills that they have learned during the day. They also experience more vivid dreams, which may be emotional or strange.
REM sleep occurs in the human body and is usually initiated by acetylcholine secretion. It can last up to an hour and is typically associated with dreaming.
During REM sleep, a part of the brain shuts off spinal cord signals. This area of the brain is known as the pons. The pons is also responsible for filtering information.
REM sleep also increases the brain’s activity. It is similar to patterns of brain activity during wakefulness. In fact, the brain’s activity during REM is higher than during NREM.
REM sleep is a key part of the human body’s processes for learning, memory, and recovery. Research has shown that children, infants, and newborns spend the most time in REM.
REM sleep is important because it is the time when new learning is committed to long-term memory. Unlike NREM, REM is not considered restful sleep.
Rapid eye movements are also linked to REM sleep. These movements are marked by a rapid decrease in the tone of muscles throughout the body. If you awake during this stage, you may experience disorientation.
Getting a good night’s sleep is essential for your brain to stay healthy. Several studies have linked low quality of sleep with increased risk for migraines and other health issues.
REM sleep is also associated with a phenomenon called the “REM rebound” effect. This is when the duration of REM sleep increases during the second half of the night.
In contrast, NREM sleep is characterized by gradually slowed brain waves. During stage 2 non-REM sleep, the heart rate and breathing rate slow down. Stage 3 non-REM sleep is referred to as delta sleep.
Stages of sleep
Understanding the stages of the sleep cycle can help you achieve a better night’s rest. A sound sleep schedule is essential for maintaining health and well-being. However, insufficient sleep can have profound effects on your thinking and emotions.
Sleep is divided into five stages. Each stage plays a different role. During each stage, your body and brain recover and relax. This is important because insufficient sleep can lead to emotional and physical problems.
The first stage of sleep is very light. Your heart rate and breathing speed down. It also helps your muscles relax. If you are disturbed during this stage, you can quickly move into the next stage. Stage 3 is the most difficult to wake up from.
As sleep continues, your body temperature and breathing rates drop. You may experience hypnic jerks. Usually, hypnic jerks are not harmful. They mimic the sensation of falling.
Eventually, your muscles start to fully relax. Rapid eye movement is another characteristic of the fourth stage. Breathing starts to pick up. In addition to these, you will begin to remember bits of images.
You may feel groggy. You may remember pieces of dreams or a sensation that you have been asleep. Some people can be awakened by a slight noise. Other people can remain oblivious to external stimuli.
REM sleep occurs after 90 minutes of sleep. REM sleep usually lasts about 10 minutes. REM sleep is associated with intense dreaming. Generally, older adults spend less time in REM sleep, while newborns and infants experience the shortest REM sleep periods.
The next stage is deep sleep. Deep sleep helps your body repair itself. This is important for your immune system and memory consolidation. Often, this stage is the final phase of the sleep cycle.
During this stage, you may experience a slow brain wave called delta sleep. These waves are so slow that they are hard to wake up from. Besides being a restorative experience, they can also cause vivid dreams.
REM sleep is important because it allows your brain and body to recharge. The REM cycle can last up to an hour.
Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep
Non-rapid eye movement sleep is the name given to the stage of sleep in which the brain’s activity is lower. In this state, the body’s muscles are completely relaxed and the heartbeat and breathing slow to the lowest possible levels.
This sleep cycle occurs four or five times a night. It starts with the light sleep phase and progressively gets deeper until the final phase, called deep sleep.
The first stage is usually short and marked by muscle relaxation and a slowing of the heart rate. During this time, you might also remember some images, and your eyes might be moving a little.
The next stage is a longer period of deep sleep that is characterized by the slowing of the heartbeat, and the eyes may not move at all. Awakening in this stage can cause disorientation.
Rapid eye movement sleep occurs in the first 90 minutes of sleep. It is associated with dreaming and is the most vivid sleep stage. It is considered to be a more wakeful state than non-REM sleep.
Stages of the sleep cycle are classified based on the ongoing brain activity that is recorded from a limited number of electrodes. Each stage affects the brain differently.
REM is associated with dreams, but it is not the only stage of sleep. In addition to REM, the body’s other stages include NREM and slow-wave sleep.
REM sleep is also considered to be a phase in which the body starts to repair itself. For instance, this phase is when the immune system is strengthened. It is important to get a good night’s rest to recover from illness or injury and to deal with stress.
One study suggested that REM sleep might play a role in memory. However, it is impossible to know whether it actually does. Studies have also shown that it is not a necessary feature of unconsciousness.
In addition, it is not clear if rapid eye movement sleep plays a role in the mental and physical recovery that is essential for healthy adults. Research in the area is still ongoing.
Slow wave sleep
The slow wave sleep cycle is the deepest phase of the sleeping hours. This phase is when the body releases restorative hormones. It is a period of relaxation and is essential for brain repair.
During the deep sleep stage, the body also releases growth hormones. Those who are suffering from insomnia are probably not getting enough of this sleep. Slow-wave sleep is crucial to memory consolidation and is vital for the healthy functioning of the body.
Sleep issues like insomnia, REM rebound, and sleep apnea are all problems associated with the slow-wave sleep cycle. Thankfully, there are supplements that can help manage the sleep cycle. These supplements can also make you fall asleep faster.
Night terrors are also a part of the slow-wave sleep cycle. These are episodes of partial waking that can last for a few seconds or minutes. They can occur multiple times during the night. Usually, individuals do not remember the episode.
Night terrors are common among children, but adults can also have them. In addition to intense fear, night terrors can include crying, screaming, and even sleepwalking.
Several studies have shown that the brain also flushes out toxic waste during this time. Scientists believe that if you have a lot of these episodes, you might be experiencing a sleep disorder. However, if you are a healthy adult, it is unlikely that you will have night terrors.
Sleep deprivation is the major cause of insomnia. Getting less sleep can negatively impact mental health and cause other health issues. Some people experience problems with their hair, skin, and memory.
Slow-wave sleep is the final stage of the sleep cycle. It is associated with slowed neuronal firing and is accompanied by low-frequency electroencephalogram (EEG) readings.
Although the average duration of the slow wave sleep phase is 40 minutes, it can be longer. Aside from slowing down the brain, it is also associated with decreased muscle tone and increased levels of human growth hormone.
Studies have also suggested that those who are sleeping in a slow-wave sleep cycle are less likely to wake up disruptively. As a result, you are less likely to have trouble getting out of bed in the morning.